Solar absorptance is a fundamental property of materials that describes their ability to absorb incident solar radiation, expressed as a ratio between absorbed and incoming energy (on a scale from 0 to 1). This characteristic plays a crucial role in applications such as solar energy harvesting, thermal insulation, and optical coatings, where controlling light and heat absorption is essential for optimizing performance and efficiency.

In many industries, accurately measuring solar absorptance is critical to achieving desired thermal and optical characteristics. For example, in solar thermal energy, high absorptance coatings, also called anti-reflective coatings, improve efficiency by maximizing sunlight absorption while minimizing reflection. In aerospace, surface coatings with engineered absorptance values help regulate spacecraft temperatures. Miscalculations in absorptance can lead to suboptimal energy utilization, overheating, or reduced performance in thermal management applications.
This article explores the tools, measurement techniques, and industry standards that define modern absorptance analysis.
What Is Solar Absorptance?
Definition
Absorptance (α) is defined as the fraction of incident radiation absorbed by a material, with values ranging from 0 (perfect reflector) to 1 (perfect absorber). This property is crucial in determining how materials interact with electromagnetic radiation, impacting thermal performance and energy efficiency. For opaque materials, the following equation can be used to derive absorptance from reflectance at a particular wavelength:
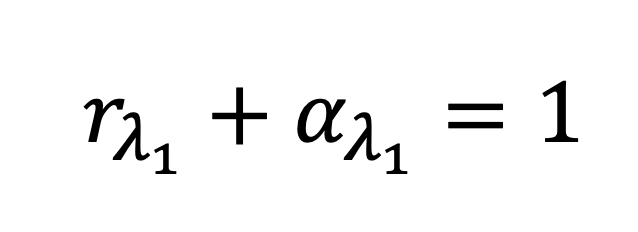
While absorptance can occur at any wavelength in the electromagnetic spectrum, solar absorptance refers to approximately 380 to 780 nanometers.
Factors Influencing Solar Absorptance
Several factors affect a material’s absorptance, including:
- Material Composition: Metals, ceramics, and polymers exhibit different absorption characteristics due to their atomic structures.
- Temperature: Emissivity values can change with temperature variations, particularly in non-metallic materials.
- Surface Finish: Rough or oxidized surfaces typically have higher absorptance than polished surfaces.
- Wavelength Dependence: Absorptance varies across different spectral ranges, making spectral analysis essential in optical applications.
Understanding these factors ensures the selection of appropriate measurement techniques and the accuracy of absorptance data in real-world applications.
Tools for Measuring Solar Absorptance
Handheld Reflectometers and Absorptance Meters
Handheld emissometers provide quick, in-field measurements of emissivity. These tools are particularly useful for field and industrial applications, which often require portability and real-time data. The ease of use enables measurement of different samples, such as standard 1-inch rounds, solar panels still in the field, or even satellites that are ready to launch. Older models, such as the 400T have been historically used in NASA spacecraft thermal control as replacements to the now outdated Gier-Dunkle DB-100 infrared reflectometer.
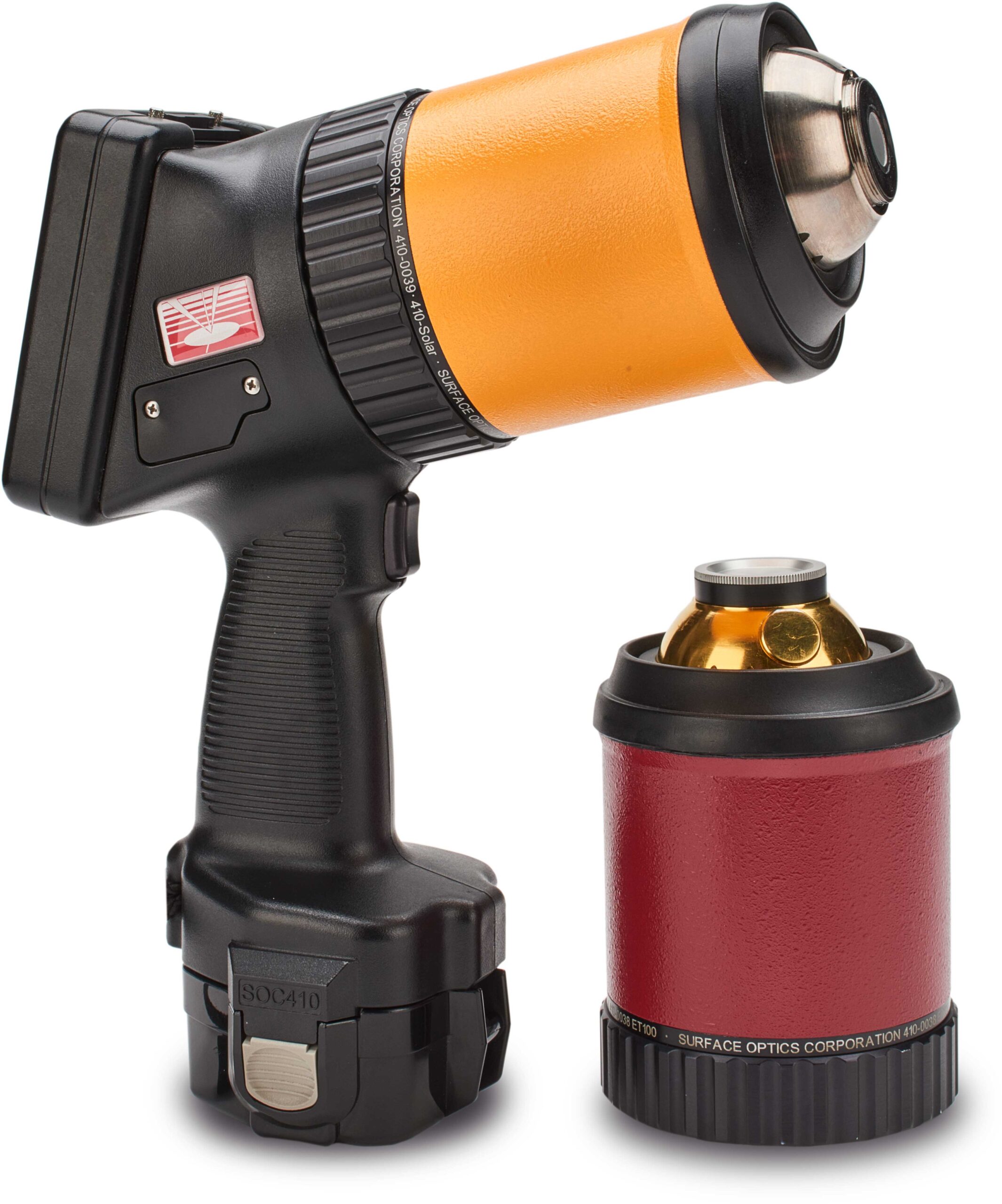

SOC-410 Vis-IR, a portable reflectometer capable of providing reflectance, solar absorptance, and thermal emissivity. This operates in the range of 335 nm – 21 microns and is used to calculate values such as α/ε and SRI. The 410 Vis-IR complies with ASTM C1549, E408, E903, and E1980.
Pros:
- Quick, real-time data collection
- Easy to operate
- Suitable for diverse material types and sample sizes
Cons
- Limited spectral resolution
- Higher uncertainty compared to lab instruments
- More assumptions in data processing
Laboratory-Based Spectrophotometers
For precise absorptance measurements, benchtop reflectometers offer controlled testing conditions and high spectral resolution. These instruments analyze how materials interact with specific wavelengths, providing detailed absorptance data essential for research and engineering applications.
Pros:
- High spectral accuracy
- Capable of measuring transmission and reflectance
- Suitable for wavelength-dependent studies
Cons
- More complex setup and operation
- Requires sample preparation
- Slower than portable devices
Hyperspectral Cameras
Hyperspectral imaging provides a powerful method for measuring and analyzing absorptance across a broad spectral range. Unlike point-based reflectometers, hyperspectral cameras capture spatially resolved spectral data, allowing for detailed reflectance and absorptance mapping across an entire surface. This capability is particularly useful in applications where material properties vary across a sample, such as in coatings, textiles, and biological materials.
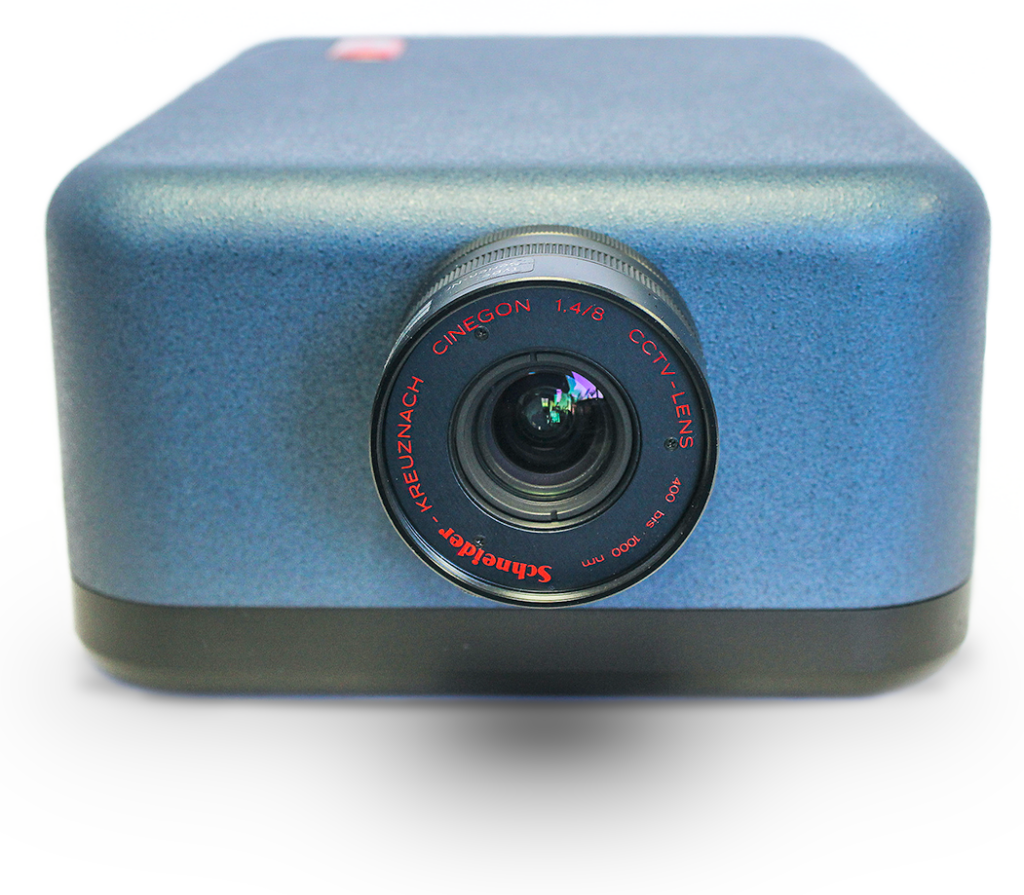

The SOC710 Hyperspectral Cameras offer advanced spectral imaging capabilities for 400 – 1700 nanometer measurements. It eliminates the need for translation stages required in traditional push-broom systems by integrating an internal scanning mechanism. This design simplifies experimental setups and improves measurement accuracy by ensuring precise synchronization of scan speed and exposure settings.
Pros:
- High spectral resolvution and dynamic range
- Wide spectral range options:
- SOC710-E and SOC710-sCMOS: 400 – 1000 nm (Visible to Near-Infrared)
- SOC710-SWIR: 900 – 1700 nm (Short-Wave Infrared)
- Internal scanning enables spatially resolved data collection without a moving stage
- Real-time imaging
Cons:
- Requires advanced data processing for full spectral analysis
- Larger data storage requirements due to hyperspectral cube format
- Slower than portable devices
Best Practices for Accurate Measurements
- Calibrate instruments regularly to ensure measurement reliability.
- Properly prepare and clean samples to avoid contamination affecting results.
- Understand limitations and proper operation of the reflectometer.
- Consider wavelength and temperature dependencies for accurate spectral data.
- Select the right instrument based on the application’s precision and portability needs.
Applications of Absorptance Measurements
1. Solar Energy Optimization
High-absorptance coatings on solar panels and thermal collectors enhance energy absorption, improving efficiency in photovoltaic and solar-thermal systems.
2. Aerospace and Defense
Engineered absorptance coatings help regulate spacecraft and aircraft surface temperatures, balancing solar heating and thermal radiation emission.
3. Building and Construction
Absorptance data informs the development of energy-efficient roofing materials and coatings to mitigate heat gain in urban environments.
4. Optical and Photonic Devices
Understanding absorptance in optical coatings is essential for applications in laser systems, infrared imaging, and sensor technology.
How We Support Solar Absorptance Menasurements
Surface Optics Corporation provides industry-leading optical instruments, offering both portable reflectometers and hyperspectral cameras. These tools ensure precise absorptance measurements in compliance with industry standards. With a wealth of expertise, our lab services help thermal and materials engineers obtain accurate, reliable data.
Questions?
We are happy to answer questions about solar absorptance measurements and provide information on our measurement services and instrumentation. Reach out today!
